|
Flat Top Beam Shaper
|
Laser beam with uniform intensity distribution over the cross section of a working plane, the so called flat-top beam, is important for: laser welding, laser micro-fabrication, laser radar, laser scanning, laser partical counting, and optical processing. We custom fabricate beam shaper at low cost that can convert an circular Gaussian beam into a circular flat-top beam. The schematic of beam shaping is shown in Fig. 1. An example of the shaped beam is given in Fig. 2 while its measured flat-top intensity distribution is shown in Fig 3.
|
|
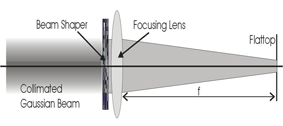 Fig 1. Beam Shaping Schematic
Fig 1. Beam Shaping Schematic
|

Fig 2. Flat-Top Beam
|
Technical reminder:
- Only circular flattop pattern can be created and input beam must be Gaussian and collimated.
- The created flattop beam size can not be arbitrarily assigned but is close to that of the normal focal spot size of the focusing lens (without beam shaper in Fig. 1). Achievable flattop beam size could be a few microns to hundreds microns using an objective lens or a general lens (if using a lens for second stage magnification, any size can be achievable).
- The input beam size and laser wavelength must match its design specs within 10% tolerances.
- Flattop beam size can be altered by changing focal length of the focusing lens, flattop location near focal plane of the corresponding lens.
- Fine alignment within 10 microns deviation between centers of input beam and the shaper is a must.
- The flattop region (depth) only exists around focal plane and the beam will be divergent after that plane. Flattop depth is similar to that of focal depth of a normal lens.
|
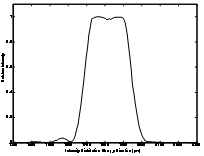
Fig 3. Intensity Distribution
|
Magnify original flattop to achieve any flattop beam size:
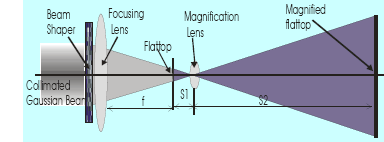
- Although the original flat-top beam size at the focal plane of the focusing lens is fixed and limited, it can be magnified to any desired size using a magnification lens, see Fig. 4. The magnification lens could be a microscope objective lens.
- The magnification ratio is S2/S1.
- The locations of the original flat-top beam and the magnified flat-top beam satisfy object-image relationship of the magnification lens.
- Fine adjustment of the magnification lens is necessary and an image acquisition device (e.g. CCD camera) may be placed at the magnified flat-top plane to monitor the adjustment.
|
|
|

